  |
  |
  |
  |
  |
  |
| @Research projects by Prof. Hideto Miyoshi and colleagues |
 |
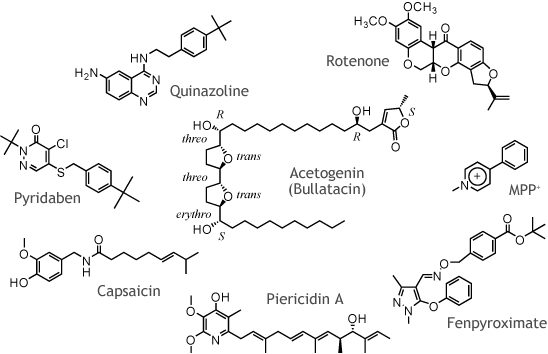
| Organic synthesis of biologically active compounds acting at respiratory system is our major projects. Our group have been synthesizing ubiquinone analogs to probe functional and structural features of various respiratory enzymes, such as mitochondrial complexes I and III and E. coli cytochrome bo and bd enzymes. Also we have been investigating the inhibition mechanism and the structure-activity relationship of various important respiratory inhibitors, such as acetogenins and antimycins. We believe that detail investigation of the inhibition mechanism of rationally designed inhibitors may provide important insights into the functional and structural features of respiratory enzymes. We are carrying out fruitful works with many collaborators using our molecular probes. |
 |
| Selected Publications |
| @Recent topics |
 |
| We synthesized a series of acetogenin analogs to identify the important structural factors required for the inhibition of bovine mitochondrial complex I. On the basis of the structure-activity relationship analysis, we proposed a model of the binding of acetogenin to the complex I. |
| References | |
|
[1] Abe, M. et al. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 14898-14906.
[PMID: 16274237]
[2] Abe, M.et al. (2008) Biochemistry 47, 6260-6266. [PMID: 18476722] |
| Through structural modification of natural acetogenins, we developed ˘lac-acetogenins, a new type of inhibitors of bovine mitochondrial complex I. Several lines of evidence revealed that the binding site of ˘lac-acetogenins is different from that of natural acetogenins as well as ordinary inhibitors such as rotenone, piericidin, and fenpyroximate. Compared to ordinary inhibitors, the level of superoxide production induced by ˘lac-acetogenins is remarkably low. |
| References | |
|
[1] Ichimaru, N. et al. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 816-825.
[PMID: 15641810]
[2] Murai, M.et al. (2006) Biochemistry 45, 9778-9787. [PMID: 16893179] [3] Murai, M.et al. (2007) Biochemistry 46, 6409-6416. [PMID: 17474759] |
| We synthesized piperazine-type new inhibitors. The inhibitory potency of the inhibitors for the reverse electron transfer in complex I was remarkably weaker than that for the forward event. The piperazines are, to the best of our knowledge, the most definitive gdirection-specifich inhibitors among diverse complex I inhibitors. |
| Reference | |
|
[1] Ichimaru, N. et al. (2008) Biochemistry 47, 10816-10826.
[PMID: 18781777]
|
| We showed that a photoreactive quinazoline, [125I]AzQ, binds to the region Asp41-Arg63 (23 amino acids) in the 49 kDa subunit of bovine mitochondrial complex I. This region in the 49 kDa subunit is a possible area of contact with the ND1 subunit. The work revealed, for the first time, the inhibitor binding site in complex I at the sub-subunit level. |
| Reference | |
|
[1] Murai, M. et al. (2009) Biochemistry 48, 688-698.
[PMID: 19128036]
|